Portal:History of science
The History of Science Portal
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Protoscience, early sciences, and natural philosophies such as alchemy and astrology during the Bronze Age, Iron Age, classical antiquity, and the Middle Ages declined during the early modern period after the establishment of formal disciplines of science in the Age of Enlightenment.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but survived in the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire. Aided by Arabic translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The transfer and assimilation of Greek and Islamic science into Western Europe from the 11th to 13th centuries revived the learning of natural philosophy in the West. Traditions of early science were also developed in ancient India and separately in ancient China, the Chinese model having influenced Vietnam, Korea and Japan before Western exploration. Among the Pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica, the Zapotec civilization established their first known traditions of astronomy and mathematics for producing calendars, followed by other civilizations such as the Maya.
Natural philosophy was transformed during the Scientific Revolution in 16th- to 17th-century Europe, as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The new science that emerged was more mechanistic in its worldview, more integrated with mathematics, and more reliable and open as its knowledge was based on a scientific method. More "revolutions" in subsequent centuries soon followed. The chemical revolution of the 18th century, for instance, introduced new quantitative methods and measurements for chemistry. In the 19th century, new perspectives regarding the conservation of energy, age of Earth, and evolution came into focus. And in the 20th century, new discoveries in genetics and physics laid the foundations for new sub disciplines such as molecular biology and particle physics. Moreover, industrial and military concerns as well as the increasing complexity of new research endeavors ushered in the era of "big science," particularly after World War II. (Full article...)
Selected article -
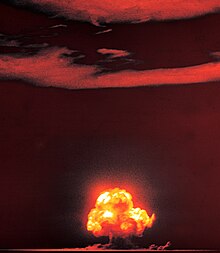
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was directed by Major General Leslie Groves of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the bombs. The Army program was designated the Manhattan District, as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the name gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. The project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys, and subsumed the program from the American civilian Office of Scientific Research and Development. The Manhattan Project employed nearly 130,000 people at its peak and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $27 billion in 2023), over 80 percent of which was for building and operating the plants that produced the fissile material. Research and production took place at more than 30 sites across the US, the UK, and Canada.
The project resulted in two types of atomic bombs, developed concurrently during the war: a relatively simple gun-type fission weapon and a more complex implosion-type nuclear weapon. The Thin Man gun-type design proved impractical to use with plutonium, so a simpler gun-type design called Little Boy was developed that used uranium-235. Three methods were employed for uranium enrichment: electromagnetic, gaseous, and thermal. In parallel with the work on uranium was an effort to produce plutonium. After the feasibility of the world's first artificial nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1, was demonstrated in 1942 at the Metallurgical Laboratory in the University of Chicago, the project designed the X-10 Graphite Reactor and the production reactors at the Hanford Site, in which uranium was irradiated and transmuted into plutonium. The Fat Man plutonium implosion-type weapon was developed in a concerted design and development effort by the Los Alamos Laboratory. (Full article...)Selected image

This famous sequence of photographs, depicting a horse in motion, was created by Eadweard Muybridge in 1904. His technique involved multiple cameras, linked by an electrical trigger, to capture many images in rapid succession. Muybridge demonstrated this and many other sets of motion photographs to the public using his zoopraxiscope, a precursor of motion pictures.
Did you know
... that the Merton Thesis—an argument connecting Protestant pietism with the rise of experimental science—dates back to Robert K. Merton's 1938 doctoral dissertation, which launched the historical sociology of science?
...that a number of scientific disciplines, such as computer science and seismology, emerged because of military funding?
...that the principle of conservation of energy was formulated independently by at least 12 individuals between 1830 and 1850?
Selected Biography -
George Bogdanovich Kistiakowsky (Russian: Георгий Богданович Кистяковский, Ukrainian: Георгій Богданович Кістяківський, romanized: Heorhii Bohdanovych Kistiakivskyi; December 1 [O.S. November 18] 1900 – December 7, 1982) was a Ukrainian-American physical chemistry professor at Harvard who participated in the Manhattan Project and later served as President Dwight D. Eisenhower's Science Advisor.
Born in Boyarka in the old Russian Empire, into "an old Ukrainian Cossack family which was part of the intellectual elite in pre-revolutionary Russia", Kistiakowsky fled his homeland during the Russian Civil War. He made his way to Germany, where he earned his PhD in physical chemistry under the supervision of Max Bodenstein at the University of Berlin. He emigrated to the United States in 1926, where he joined the faculty of Harvard University in 1930, and became a citizen in 1933. (Full article...)Selected anniversaries
- 1561 - Birth of Philippe van Lansberge, Dutch astronomer (d. 1632)
- 1609 - Galileo Galilei demonstrates his first telescope to Venetian lawmakers
- 1822 - Death of William Herschel, German-born astronomer (b. 1738)
- 1867 - Death of Michael Faraday, English scientist (b. 1791)
- 1898 - Birth of Helmut Hasse, German mathematician (d. 1975)
- 1900 - Birth of Hans Adolf Krebs, German physician and biochemist; Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1981)
- 1908 - Death of Henri Becquerel, French physicist, Nobel laureate (b. 1852)
- 1928 - Birth of Herbert Kroemer, German-born physicist, Nobel Prize laureate
- 1956 - Death of Alfred Kinsey, American research biologist (b. 1894)
- 1964 - Birth of Maxim Kontsevich, Russian mathematician
Related portals
Topics
General images
Subcategories
Things you can do
Help out by participating in the History of Science Wikiproject (which also coordinates the histories of medicine, technology and philosophy of science) or join the discussion.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus